Flea bite in Child
Synopsis

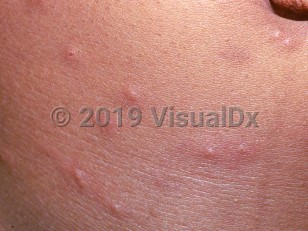
Fleas are small, 1-4 mm in length, and blackish-brown. Although wingless, fleas are still capable of taking giant leaps, jumping to a height of several meters. Adult fleas feed only on blood and are capable of living long periods without feeding. Fleas most often bite people around the legs and the ankles. The flea injects antigenic saliva after piercing the skin with its mandibles. The bites, which are felt immediately, become increasingly irritated and may remain sore for as long as a week. Itching may be generalized or just at the site of the bites.
Flea bites produce a variety of effects, ranging from a transient wheal to prolonged symptoms that may last for years depending on the sensitivity of the person bitten. Children aged younger than 10 are generally more sensitive than older people, as people tend to become desensitized by repeated exposure over time. Flea bites in children produce a papular urticaria in which recurrent or chronic pruritic papules occur on the exposed skin areas. Patients with hypersensitivity may also develop bullous reactions.
Codes
W57.XXXA – Bitten or stung by nonvenomous insect and other nonvenomous arthropods, initial encounter
SNOMEDCT:
262551003 – Flea bites
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
 Patient Information for Flea bite in Child
Patient Information for Flea bite in Child- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient