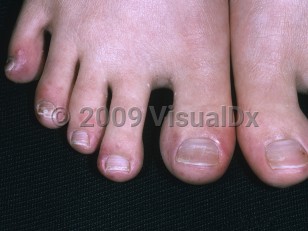
Cryofibrinogenemia
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

A familial autosomal dominant form has also been reported. In a 2020 study, cryofibrinogenemia was detected in two-thirds of 54 patients with COVID chilblains. More studies are needed to confirm that cryofibrinogenemia is implicated in the pathogenesis of chilblains in COVID-19 patients.
Cryofibrinogenemia may be treatable and reversible, with a relatively prompt resolution of skin lesions with immunosuppressive therapy.
Codes
D89.2 – Hypergammaglobulinemia, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
10934005 – Cryofibrinogenemia
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required