Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

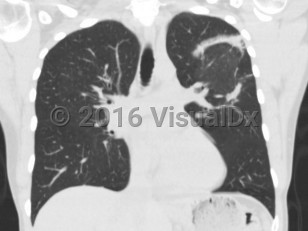
Patients typically present with relatively short duration of symptoms (weeks to months) including a persistent nonproductive cough, dyspnea, fever, malaise, weight loss, and occasionally other influenza-like symptoms (nasal congestion, headache, chills and sweats, sore throat, myalgia). Hemoptysis is uncommon. Physical examination reveals inspiratory crackles in a majority of patients, and radiographic findings include peripheral, patchy bilateral opacities.
History of stigmata of extrapulmonary connective tissue disease and/or medication exposure should be sought to differentiate COP from other idiopathic interstitial pneumonitides.
Codes
J84.116 – Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
SNOMEDCT:
719218000 – Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:06/19/2022