DFs are often solitary, though any individual may have more than one. Rarely, multiple eruptive dermatofibromas (MEDFs) may be seen. MEDF is arbitrarily defined as the presence of 5 to 15 or more DFs developing in less than a 4-month period. MEDF has been reported to occur in individuals with HIV infection; autoimmune disease, most frequently systemic lupus erythematosus; neoplastic disease; and in pregnant individuals. Multiple clustered dermatofibroma (MCDF) is a rare entity that develops in the first to third decades, where 15 or more DFs cluster together to form a plaque, most often on the lower half of the body.
In rare families with dominantly inherited DF, missense mutation in the factor XIII A-subunit has been detected.
Some rare variants of DFs, particularly aneurysmal, cellular, and atypical fibrous histiocytomas, are characterized by an increased risk of local recurrence compared to conventional DFs:
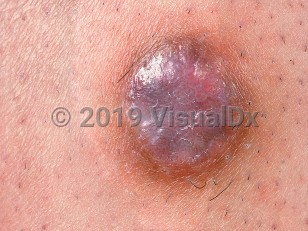
- Aneurysmal DF (hemorrhagic or hemosiderotic DF): This variant represents less than 2% of DFs. It mainly arises in young adults and shows rapid growth. Lesions tend to be larger than typical DFs, with a cystic consistency and a pigmented or vascular appearance. The rate of recurrence is about 20% following excision.
- Cellular DF: This variant represents less than 5% of cutaneous fibrous histiocytomas. Although more common in the extremities, it can sometimes occur on the face, ears, hands, and feet. In comparison to common DFs, cellular DFs are larger in size with a predilection for men and a higher recurrence rate of up to 26% in some studies.
- Atypical DF (DF with monster cells): This variant is usually seen in middle-aged adults. Lesions are slightly larger than 1 cm in diameter and are clinically similar to common DFs.



 Patient Information for
Patient Information for