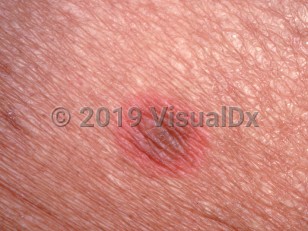
Fixed drug eruption - Anogenital in
See also in: Overview,Cellulitis DDx,Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

FDE is most commonly solitary, but some individuals may develop multiple patches. There may be an increasing number of patches seen with each exposure. Healing with postinflammatory hyperpigmentation is common.
Numerous drugs have been implicated in causing FDE. The most commonly associated drug classes for FDE in the anogenital region are also the most frequently seen culprit medications for FDE in general. These medication classes include antibiotics, in particular sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and tetracyclines, and NSAIDs, including naproxen, ibuprofen, and celecoxib. Other drugs implicated in FDE include amoxicillin, erythromycin, metronidazole, fluconazole, paracetamol (acetaminophen), cetirizine, hydroxyzine, methylphenidate, oral contraceptives, quinine, and phenolphthalein. Biologic agents including ustekinumab, adalimumab, and abatacept have been reported to cause fixed drug eruptions. A nonpigmenting version of this condition is seen with pseudoephedrine.
Codes
L27.1 – Localized skin eruption due to drugs and medicaments taken internally
SNOMEDCT:
73692007 – Fixed drug eruption
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:02/02/2021
 Patient Information for Fixed drug eruption - Anogenital in
Patient Information for Fixed drug eruption - Anogenital in - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient