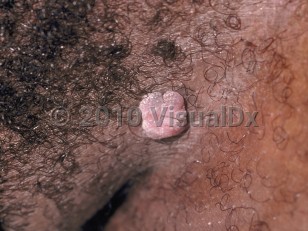
Genital wart - Anogenital in
See also in: OverviewSynopsis

Transmission of HPV infection can occur through either direct contact, autoinoculation, or fomite transfer. The average incubation period for warts ranges from 2-3 months but can extend up to 1 year. Most lesions are symptomless; however, associated symptoms can include itching, bleeding, and dyspareunia.
The highest risk population for HPV infection is sexually active women younger than 26 years. However, HPV infection can affect patients of any sex and a wide span of ages from infants to the elderly.
During pregnancy, condyloma acuminata can demonstrate rapid growth. The presence of condyloma acuminata has been associated with higher cesarean delivery rates. There is a small risk of transmission to the infant, with studies estimating the risk of maternal-child transmission with development of the disease in the child to be 1 in 1500.
In immunosuppressed patients, warts are thought to proliferate due to suppressed cellular immunity and have a risk of developing cancer. An increased prevalence of anogenital warts is noted in this population. Recurrences are common and response to treatment is impaired.
Related topic: oral mucosal wart
Codes
A63.0 – Anogenital (venereal) warts
SNOMEDCT:
240542006 – Condyloma acuminatum
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:09/23/2021
 Patient Information for Genital wart - Anogenital in
Patient Information for Genital wart - Anogenital in - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient