Herpes simplex virus - Anogenital in
See also in: Overview,Cellulitis DDxAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

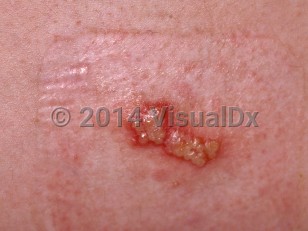
Genital herpes simplex is a viral infection that is caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). It is frequently seen in sexually active adolescents but can also occur in younger children. Nonsexual acquisition by vertical transmission can take place at the time of birth, by hand contact during diapering, or by autoinoculation. However, new genital herpetic lesions in children without a history of perinatal acquisition who have independent toileting are suspicious for abuse and should be evaluated. Both types may be due to sexual abuse. An associated history of recurrent herpes gingivostomatitis or herpetic whitlow argues against abuse.
Infection by the virus is acquired from direct contact with active lesions, and symptoms develop within 5-10 days of initial contact. However, it is important to note that even when asymptomatic, a person sheds the virus and so can transmit the disease to another. In some adolescents, primary infection can be severe and include symptoms of aseptic meningitis such as fever, headache, stiff neck, and photophobia. In girls, there can be severe local symptoms of pain, dysuria, and vaginal discharge.
Childhood sexual abuse is a problem of epidemic proportions affecting children of all ages and of all economic and cultural backgrounds. Although awareness is increasing, it is often challenging to differentiate findings attributable to child abuse from those of other benign anogenital skin conditions.
Infection by the virus is acquired from direct contact with active lesions, and symptoms develop within 5-10 days of initial contact. However, it is important to note that even when asymptomatic, a person sheds the virus and so can transmit the disease to another. In some adolescents, primary infection can be severe and include symptoms of aseptic meningitis such as fever, headache, stiff neck, and photophobia. In girls, there can be severe local symptoms of pain, dysuria, and vaginal discharge.
Childhood sexual abuse is a problem of epidemic proportions affecting children of all ages and of all economic and cultural backgrounds. Although awareness is increasing, it is often challenging to differentiate findings attributable to child abuse from those of other benign anogenital skin conditions.
Codes
ICD10CM:
B00.1 – Herpesviral vesicular dermatitis
SNOMEDCT:
88594005 – Herpes simplex
B00.1 – Herpesviral vesicular dermatitis
SNOMEDCT:
88594005 – Herpes simplex
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:12/14/2016
Last Updated:02/04/2016
Last Updated:02/04/2016
 Patient Information for Herpes simplex virus - Anogenital in
Patient Information for Herpes simplex virus - Anogenital in
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Herpes simplex virus - Anogenital in
See also in: Overview,Cellulitis DDx