Leprosy-Lucio phenomena
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Lucio phenomenon is a rare reaction seen in patients with multibacillary leprosy due to endothelial invasion of Mycobacterium leprae. It is most commonly seen in Mexico and Central America, although cases have been reported in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
The pathogenesis is thought to be mediated by complement activation of immune-complex deposition. Leprosy bacilli invade blood vessel endothelium, causing endothelial proliferation and narrowing of the vascular lumen. Reports have suggested that certain stressors, such as pregnancy, concurrent infection, and cold weather, may precipitate Lucio phenomenon.
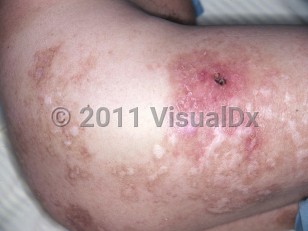
Manifestations of Lucio phenomenon typically occur 1-3 years after onset of leprosy. Patients present with sudden onset of painful violaceous plaques that may become hemorrhagic, bullous, and then ulcerated. Subcutaneous nodules may be a feature. The lower extremities are affected most frequently, but the forearms and buttocks may also be involved. Ulcers heal with atrophic scars after 2-4 weeks. Although constitutional symptoms are rare, patients may have fever, myalgia, or arthralgia. Lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and leukocytosis with neutrophilia may be seen.
Lucio phenomenon may be complicated by sepsis from superadded infection.
The pathogenesis is thought to be mediated by complement activation of immune-complex deposition. Leprosy bacilli invade blood vessel endothelium, causing endothelial proliferation and narrowing of the vascular lumen. Reports have suggested that certain stressors, such as pregnancy, concurrent infection, and cold weather, may precipitate Lucio phenomenon.
Manifestations of Lucio phenomenon typically occur 1-3 years after onset of leprosy. Patients present with sudden onset of painful violaceous plaques that may become hemorrhagic, bullous, and then ulcerated. Subcutaneous nodules may be a feature. The lower extremities are affected most frequently, but the forearms and buttocks may also be involved. Ulcers heal with atrophic scars after 2-4 weeks. Although constitutional symptoms are rare, patients may have fever, myalgia, or arthralgia. Lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and leukocytosis with neutrophilia may be seen.
Lucio phenomenon may be complicated by sepsis from superadded infection.
Codes
ICD10CM:
A30.8 – Other forms of leprosy
SNOMEDCT:
228007 – Lucio phenomenon
A30.8 – Other forms of leprosy
SNOMEDCT:
228007 – Lucio phenomenon
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:01/14/2018
Last Updated:01/28/2018
Last Updated:01/28/2018