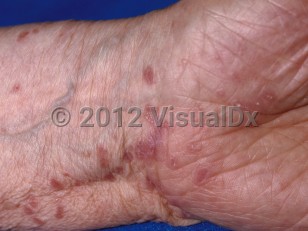
Lichen planus - Anogenital in
See also in: Overview,Nail and Distal DigitAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

See oral lichen planus for oral mucosal presentation and lichen planopilaris for scalp presentation.
Certain medications may cause a lichenoid drug eruption, which is indistinguishable from typical LP.
Codes
L43.9 – Lichen planus, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
4776004 – Lichen planus
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:05/12/2019
 Patient Information for Lichen planus - Anogenital in
Patient Information for Lichen planus - Anogenital in - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient