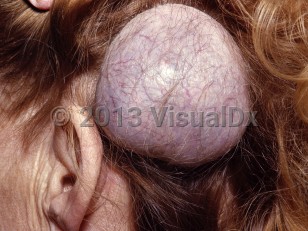
Meningioma
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Meningiomas are typically slow growing and benign, but the condition can be complicated by size and rate of growth and compression of surrounding brain tissue. In rare cases, meningiomas can become malignant. Small tumors may be asymptomatic. Large tumors may cause a variety of symptoms including headaches, focal seizures, weakness, numbness, incontinence, apathy, aphasia, anosmia, and increased intracranial pressure.
Risk factors include hormonal factors (progesterone > estrogen > androgens), genetic syndromes such as neurofibromatosis type 2, and exposure to ionizing radiation. Prognosis is generally good, with a 5-year survival rate of 70%. Patients with a history of radiation exposure tend to have more aggressive and atypical tumors with a worse prognosis.
Codes
D32.9 – Benign neoplasm of meninges, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
302820008 – Intracranial meningioma
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:04/18/2018