Molluscum contagiosum - Anogenital in
See also in: Overview,External and Internal EyeAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

This summary discusses adult patients. Molluscum contagiosum in children is addressed separately.
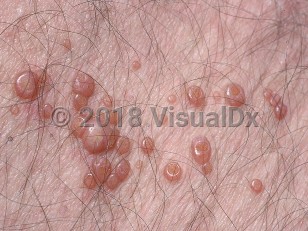
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection caused by a DNA poxvirus. It manifests as smooth, firm papules with a central umbilication. Genital lesions are most commonly spread by sexual contact and tend to be located on the hair-bearing regions of the mons and inguinal creases. The labia majora, inner thighs, and buttocks may also be involved.
Molluscum contagiosum may also be spread by direct contact (most often in children) and autoinoculation (ie, shaving). Infections have also been associated with swimming pool facilities via fomites.
Many cases are asymptomatic, but there can be surrounding irritation and pruritus. In the immunocompetent host, the disease tends to be self-limited, but papules may persist for several months and up to 2 years before disappearing.
In cases of underlying immunodeficiency, such as HIV disease, molluscum may be widespread or large, atypical papules and/or plaques may be seen.
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection caused by a DNA poxvirus. It manifests as smooth, firm papules with a central umbilication. Genital lesions are most commonly spread by sexual contact and tend to be located on the hair-bearing regions of the mons and inguinal creases. The labia majora, inner thighs, and buttocks may also be involved.
Molluscum contagiosum may also be spread by direct contact (most often in children) and autoinoculation (ie, shaving). Infections have also been associated with swimming pool facilities via fomites.
Many cases are asymptomatic, but there can be surrounding irritation and pruritus. In the immunocompetent host, the disease tends to be self-limited, but papules may persist for several months and up to 2 years before disappearing.
In cases of underlying immunodeficiency, such as HIV disease, molluscum may be widespread or large, atypical papules and/or plaques may be seen.
Codes
ICD10CM:
B08.1 – Molluscum contagiosum
SNOMEDCT:
40070004 – Molluscum contagiosum
B08.1 – Molluscum contagiosum
SNOMEDCT:
40070004 – Molluscum contagiosum
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:05/05/2021
Last Updated:06/07/2021
Last Updated:06/07/2021
 Patient Information for Molluscum contagiosum - Anogenital in
Patient Information for Molluscum contagiosum - Anogenital in
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Molluscum contagiosum - Anogenital in
See also in: Overview,External and Internal Eye