Oral frictional hyperkeratosis - Oral Mucosal Lesion
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

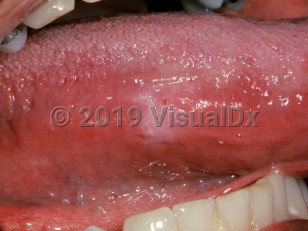
Oral frictional hyperkeratosis is a benign white lesion of the oral mucosa that is caused by chronic trauma to the site. This tends to occur in adults.
The area is asymptomatic.
This occurs on the maxillary and mandibular alveolar ridges particularly after extraction of teeth, and particularly in the area of extracted mandibular third molars on the retromolar pad area. The alveolar ridge mucosa that had previously been "protected" from food impingement is now exposed to trauma and becomes hyperkeratotic as a protective mechanism.
However, other sites may be affected depending on the circumstance. For example, a sharp or broken cusp that rubs against the buccal mucosa or lateral/ventral tongue may cause an area of hyperkeratosis.
These areas take months to develop and they persist as long as the traumatic events persist.
Related topic: Chronic cheek chewing
The area is asymptomatic.
This occurs on the maxillary and mandibular alveolar ridges particularly after extraction of teeth, and particularly in the area of extracted mandibular third molars on the retromolar pad area. The alveolar ridge mucosa that had previously been "protected" from food impingement is now exposed to trauma and becomes hyperkeratotic as a protective mechanism.
However, other sites may be affected depending on the circumstance. For example, a sharp or broken cusp that rubs against the buccal mucosa or lateral/ventral tongue may cause an area of hyperkeratosis.
These areas take months to develop and they persist as long as the traumatic events persist.
Related topic: Chronic cheek chewing
Codes
ICD10CM:
K13.79 – Other lesions of oral mucosa
SNOMEDCT:
235034000 – Oral frictional keratosis
K13.79 – Other lesions of oral mucosa
SNOMEDCT:
235034000 – Oral frictional keratosis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:06/10/2018