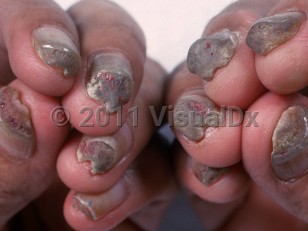
PC is classified into 4 subtypes:
- Type 1 (also known as Jadassohn-Lewandowski syndrome) (keratin-16 gene mutation) is the most common subtype, representing 56% of PC patients. Patients present with subungual hyperkeratosis and progressive thickening of the fingernails and toenails beginning a few months after birth. The distal third of the nail plate is thickened with increased transverse curvature. Onycholysis is secondary to subungual hyperkeratosis. Patients often present with palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, follicular hyperkeratosis, and oral leukokeratoses.
- Type 2 (also known as Jackson-Lawler syndrome) (keratin-17 gene mutations) account for 25% of patients with PC. In addition to the findings seen in PC type 1, type 2 patients present with bullae and hyperhidrosis of the palms and soles, natal teeth, and steatocystoma multiplex.
- Type 3 patients (keratin-6A gene mutations), in addition to type 1 findings, also present with angular cheilitis, corneal dyskeratosis, and cataracts. These patients account for 12% of PC cases.
- Type 4 patients (keratin-6B gene mutations), in addition to type 1 findings, also present with laryngeal lesions, hoarse voice, intellectual disability, and alopecia. These patients account for 7% of PC cases.