Papilledema - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

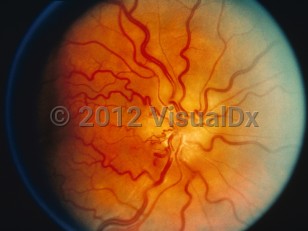
Papilledema can lead to blindness, but perhaps even more importantly, it can be the first sign of a mass in the brain. Disorders that can cause papilledema include intracranial masses, cerebritis or meningitis, subarachnoid or subdural hemorrhage, and pseudotumor cerebri (idiopathic intracranial hypertension).
The optic nerve appears swollen in both eyes, though in the early stages it may be asymmetric. Patients may notice blurred vision that may come and go. With chronic papilledema, there can be progressive visual field loss with eventual loss of central acuity. In chronic papilledema, the nerve may be atrophic with attenuated blood vessels and not show signs of swelling. Other signs or symptoms of elevated intracranial pressure such as headache, nausea, vomiting, diplopia, ataxia, or altered consciousness may occur as well.
Codes
H47.10 – Unspecified papilledema
SNOMEDCT:
423341008 – Optic disc edema
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required