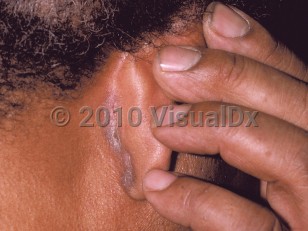
Seborrheic dermatitis in Child
See also in: Anogenital,Hair and ScalpAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

The yeast Malassezia has long been regarded as the central predisposing factor to disease development. Malassezia is a normal component of skin flora, but in individuals with seborrheic dermatitis, the yeast invades the stratum corneum, resulting in free fatty acid formation and the activation of the inflammatory cascade. Changes in the skin microbiome have also been implicated in pathogenesis. Additional factors related to the environment such as low temperatures and humidity have been identified as potential triggers.
Codes
L21.9 – Seborrheic dermatitis, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
50563003 – Seborrheic dermatitis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:04/06/2023
 Patient Information for Seborrheic dermatitis in Child
Patient Information for Seborrheic dermatitis in Child- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient