Secondary syphilis - Hair and Scalp
See also in: Overview,Anogenital,Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Syphilis crisis in the United States: Syphilis and congenital syphilis cases have been surging nationwide, with an 80% increase in total syphilis cases between 2018 and 2022. Serologic testing is the primary means of diagnosing, staging, and managing syphilis. Testing should be done for any sexually active patient in whom syphilis is suspected or who has new, unexplained symptoms. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of syphilis can prevent systemic complications, including ocular involvement and permanent blindness.
Secondary syphilis is the second stage of the infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum, which has spread hematogenously throughout the entire body. It typically occurs 3-10 weeks after the appearance of the primary syphilitic chancre.
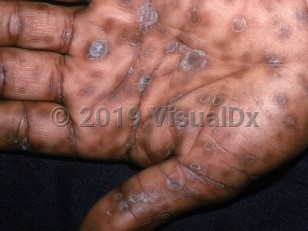
Secondary syphilis can present with varied manifestations. Patients generally develop constitutional symptoms including malaise, appetite loss, fever, headache, stiff neck, myalgias, pharyngitis, and flu-like symptoms. Generalized lymphadenopathy is typically present. Cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis may include a generalized rash that includes the palms and soles. Condyloma lata (gray, broad, papular lesions) may be seen in moist anogenital locations or in the mouth. They are teeming with spirochetes and are, therefore, extremely infectious. Gastric ulcers may occur. Ocular symptoms may include lacrimation, photophobia, and red, painful eyes.
The second stage of syphilis can have varied manifestations with respect to the hair and scalp. Patchy alopecia with a "moth-eaten" appearance can be observed on the scalp and facial hair. Telogen effluvium can be present. Syphilitic papules may line the scalp margin, known as corona veneris.
The lesions of secondary syphilis resolve in 3-12 weeks, with or without treatment. If left untreated, up to 25% of patients will relapse within the first 2 years.
Immunocompromised patient considerations: HIV infection can alter the clinical presentation of syphilis. Manifestations include multiple chancres, atypical cutaneous eruptions, increased severity of organ involvement (such as hepatitis and glomerulonephritis), and rapidly developing arteritis and neurosyphilis. Neurosyphilis can occur at any stage of syphilis.
Related topics: primary syphilis, tertiary syphilis, early congenital syphilis, late congenital syphilis, ocular syphilis
Secondary syphilis is the second stage of the infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum, which has spread hematogenously throughout the entire body. It typically occurs 3-10 weeks after the appearance of the primary syphilitic chancre.
Secondary syphilis can present with varied manifestations. Patients generally develop constitutional symptoms including malaise, appetite loss, fever, headache, stiff neck, myalgias, pharyngitis, and flu-like symptoms. Generalized lymphadenopathy is typically present. Cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis may include a generalized rash that includes the palms and soles. Condyloma lata (gray, broad, papular lesions) may be seen in moist anogenital locations or in the mouth. They are teeming with spirochetes and are, therefore, extremely infectious. Gastric ulcers may occur. Ocular symptoms may include lacrimation, photophobia, and red, painful eyes.
The second stage of syphilis can have varied manifestations with respect to the hair and scalp. Patchy alopecia with a "moth-eaten" appearance can be observed on the scalp and facial hair. Telogen effluvium can be present. Syphilitic papules may line the scalp margin, known as corona veneris.
The lesions of secondary syphilis resolve in 3-12 weeks, with or without treatment. If left untreated, up to 25% of patients will relapse within the first 2 years.
Immunocompromised patient considerations: HIV infection can alter the clinical presentation of syphilis. Manifestations include multiple chancres, atypical cutaneous eruptions, increased severity of organ involvement (such as hepatitis and glomerulonephritis), and rapidly developing arteritis and neurosyphilis. Neurosyphilis can occur at any stage of syphilis.
Related topics: primary syphilis, tertiary syphilis, early congenital syphilis, late congenital syphilis, ocular syphilis
Codes
ICD10CM:
A51.39 – Other secondary syphilis of skin
SNOMEDCT:
240557004 – Secondary syphilis
A51.39 – Other secondary syphilis of skin
SNOMEDCT:
240557004 – Secondary syphilis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:09/02/2020
Last Updated:04/03/2024
Last Updated:04/03/2024
 Patient Information for Secondary syphilis - Hair and Scalp
Patient Information for Secondary syphilis - Hair and Scalp
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today

Secondary syphilis - Hair and Scalp
See also in: Overview,Anogenital,Oral Mucosal Lesion