Chronic graft-versus-host disease in Child
See also in: Nail and Distal Digit,Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) refers to multiorgan dysfunction resulting from the introduction of foreign immunocompetent lymphocytes or bone marrow tissue (the graft) into an immunologically defective host. Most GVHD occurs in individuals who have undergone allogeneic bone marrow transplants, but it may occur in solid organ transplant and blood transfusion recipients.
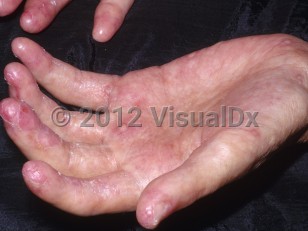
Cutaneous GVHD has both an acute and a chronic form. Acute GVHD normally occurs within 2-4 weeks of stem cell infusion and typically presents as a morbilliform eruption that may progress to erythroderma or, rarely, a toxic epidermal necrolysis-like picture.
Chronic cutaneous GVHD usually presents with mucocutaneous manifestations a mean of 4 months after transplantation. The incidence of chronic GVHD is estimated to be 60%-70% in recipients of allogeneic stem cell transplants with mismatched and unrelated donors and approximately 30% in recipients of fully histocompatible sibling donor transplants. Chronic GVHD is occasionally triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, physical trauma, varicella zoster virus, or Borrelia infection. Activation of host antigen-presenting cells (APC) triggers a cytotoxic donor T-effector response. Thymic injury with subsequent autoreactive and alloreactive T-lymphocyte proliferation and a dysregulated TH17 response lead to macrophage and fibroblast activation with altered diffuse tissue repair and fibrosis.
Almost all chronic GVHD patients will have skin involvement. Oral mucosal, hepatic, and ocular involvement is also common. The gastrointestinal (GI) tract and the lungs, as well as the peripheral nervous and musculoskeletal systems, may also be affected. Chronic GVHD increases the overall risk of systemic and recurrent bacterial infections.
GVHD is a major source of morbidity and mortality among transplant recipients. The risk of developing chronic GVHD increases with advancing age, prior acute GVHD, history of splenectomy, and donor or recipient cytomegalovirus seropositivity. On the other hand, chronic GVHD is associated with beneficial graft-versus-tumor effects and reduced risk of leukemia relapse, especially with more severe chronic GVHD.
Cutaneous GVHD has both an acute and a chronic form. Acute GVHD normally occurs within 2-4 weeks of stem cell infusion and typically presents as a morbilliform eruption that may progress to erythroderma or, rarely, a toxic epidermal necrolysis-like picture.
Chronic cutaneous GVHD usually presents with mucocutaneous manifestations a mean of 4 months after transplantation. The incidence of chronic GVHD is estimated to be 60%-70% in recipients of allogeneic stem cell transplants with mismatched and unrelated donors and approximately 30% in recipients of fully histocompatible sibling donor transplants. Chronic GVHD is occasionally triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, physical trauma, varicella zoster virus, or Borrelia infection. Activation of host antigen-presenting cells (APC) triggers a cytotoxic donor T-effector response. Thymic injury with subsequent autoreactive and alloreactive T-lymphocyte proliferation and a dysregulated TH17 response lead to macrophage and fibroblast activation with altered diffuse tissue repair and fibrosis.
Almost all chronic GVHD patients will have skin involvement. Oral mucosal, hepatic, and ocular involvement is also common. The gastrointestinal (GI) tract and the lungs, as well as the peripheral nervous and musculoskeletal systems, may also be affected. Chronic GVHD increases the overall risk of systemic and recurrent bacterial infections.
GVHD is a major source of morbidity and mortality among transplant recipients. The risk of developing chronic GVHD increases with advancing age, prior acute GVHD, history of splenectomy, and donor or recipient cytomegalovirus seropositivity. On the other hand, chronic GVHD is associated with beneficial graft-versus-tumor effects and reduced risk of leukemia relapse, especially with more severe chronic GVHD.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D89.811 – Chronic graft-versus-host disease
SNOMEDCT:
402356004 – Chronic graft-versus-host disease
D89.811 – Chronic graft-versus-host disease
SNOMEDCT:
402356004 – Chronic graft-versus-host disease
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:11/15/2022
Last Updated:01/16/2023
Last Updated:01/16/2023
Chronic graft-versus-host disease in Child
See also in: Nail and Distal Digit,Oral Mucosal Lesion