Cutis verticis gyrata - Hair and Scalp
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

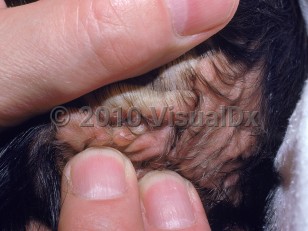
Cutis verticis gyrata (CVG), also known as bulldog scalp syndrome, paquidermia verticis gyrata, and cutis verticis plicata, is a benign scalp skin condition characterized by skin folds and furrows that mimic brain gyri and sulci. Symmetric ridges and grooves are often arranged anteroposteriorly on the vertex and occiput; however, they may involve the parietal and/or temporal scalp. CVG is rare and has an approximate prevalence of 1 in 100 000 males and 0.26 in 100 000 females. Currently, the etiology of CVG is not well understood. There are three categories of CVG: primary essential, primary nonessential, and secondary.
Primary essential CVG presents only as scalp folds and has no associated findings. It has a male predominance with onset during or after puberty. Ninety percent of patients diagnosed are older than 30.
In primary nonessential CVG, patients have neurologic, psychiatric, or ophthalmologic comorbidities (eg, intellectual disability, seizures, schizophrenia, and cataracts). This form accounts for approximately 0.5% of cases, and there is also a male predominance by a ratio of 6:1. Most patients develop symptoms after puberty.
Secondary CVG is due to inflammatory, neoplastic, or systemic conditions that lead to a cellular infiltration of the dermis, which gives rise to the corrugated appearance of the scalp. Scalp folds and furrows tend to be more asymmetric and disordered in distribution. Local inflammatory conditions of the scalp that can give rise to CVG include eczema, psoriasis, and folliculitis. Systemic conditions that are associated with secondary CVG include acromegaly, myxedema, Graves disease, amyloidosis, and syphilis. Secondary CVG has also been associated with Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and fragile X syndrome. Secondary CVG affects both sexes equally and can appear at any age, although it rarely presents in childhood.
Primary essential CVG presents only as scalp folds and has no associated findings. It has a male predominance with onset during or after puberty. Ninety percent of patients diagnosed are older than 30.
In primary nonessential CVG, patients have neurologic, psychiatric, or ophthalmologic comorbidities (eg, intellectual disability, seizures, schizophrenia, and cataracts). This form accounts for approximately 0.5% of cases, and there is also a male predominance by a ratio of 6:1. Most patients develop symptoms after puberty.
Secondary CVG is due to inflammatory, neoplastic, or systemic conditions that lead to a cellular infiltration of the dermis, which gives rise to the corrugated appearance of the scalp. Scalp folds and furrows tend to be more asymmetric and disordered in distribution. Local inflammatory conditions of the scalp that can give rise to CVG include eczema, psoriasis, and folliculitis. Systemic conditions that are associated with secondary CVG include acromegaly, myxedema, Graves disease, amyloidosis, and syphilis. Secondary CVG has also been associated with Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and fragile X syndrome. Secondary CVG affects both sexes equally and can appear at any age, although it rarely presents in childhood.
Codes
ICD10CM:
L91.8 – Other hypertrophic disorders of the skin
Q82.8 – Other specified congenital malformations of skin
SNOMEDCT:
51603000 – Cutis verticis gyrata
L91.8 – Other hypertrophic disorders of the skin
Q82.8 – Other specified congenital malformations of skin
SNOMEDCT:
51603000 – Cutis verticis gyrata
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:01/09/2022
Last Updated:01/10/2022
Last Updated:01/10/2022