Peripheral arterial disease
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

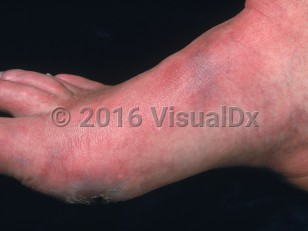
Symptoms develop when the metabolic demand of tissues is greater than vessels are able to deliver. Most patients with PAD are asymptomatic. In those who develop symptoms, look for extremity pain with activity that is relieved with rest (claudication), limb ischemia with the development of ulcers or gangrenous lesions, or critical acute limb ischemia leading to pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia, and poikilothermia.
Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis that can lead to narrowing of blood vessels. When atherosclerotic plaques involve 70%-80% of the luminal diameter, blood flow may become limited, particularly during times of physical exertion and increased demand. Plaque rupture may cause occlusion of coronary vessels or cerebrovascular vessels, leading to ischemia and infarction that present as myocardial infarctions and strokes, respectively.
Codes
I73.9 – Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
399957001 – Peripheral arterial occlusive disease
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:09/11/2019
 Patient Information for Peripheral arterial disease
Patient Information for Peripheral arterial disease - Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient