Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

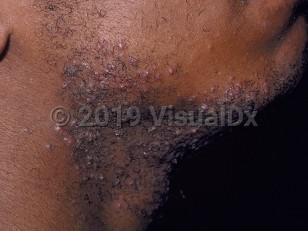
Pseudofolliculitis barbae, commonly known as "shaving bumps," is a chronic inflammatory disease of hair-bearing areas incited by shaving. It frequently occurs among populations where naturally curly hair is common. The close shaving of curly hair causes the hair to penetrate the wall of the follicle and extend into the dermis as it grows back or curves back on itself and pierces the skin, such as with an ingrown hair. The condition is more common among Black men, particularly policemen and military personnel, who may be required to be clean shaven.
Methods of close shaving that predispose to the development of pseudofolliculitis barbae include using razors with multiple blades, plucking hairs with tweezers, shaving against the grain of hair growth, and pulling the skin taut while shaving. Pseudofolliculitis barbae is primarily a cosmetic concern, but it can lead to scarring, infection, hyperpigmentation, and keloid formation.
Pseudofolliculitis pubis is a similar condition that occurs in the genital area after pubic hair is shaved. Shaving of the axillae may cause a similar condition.
Methods of close shaving that predispose to the development of pseudofolliculitis barbae include using razors with multiple blades, plucking hairs with tweezers, shaving against the grain of hair growth, and pulling the skin taut while shaving. Pseudofolliculitis barbae is primarily a cosmetic concern, but it can lead to scarring, infection, hyperpigmentation, and keloid formation.
Pseudofolliculitis pubis is a similar condition that occurs in the genital area after pubic hair is shaved. Shaving of the axillae may cause a similar condition.
Codes
ICD10CM:
L73.1 – Pseudofolliculitis barbae
SNOMEDCT:
399205006 – Pseudofolliculitis barbae
L73.1 – Pseudofolliculitis barbae
SNOMEDCT:
399205006 – Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:02/09/2022
Last Updated:02/10/2022
Last Updated:02/10/2022
 Patient Information for Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Patient Information for Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Premium Feature
VisualDx Patient Handouts
Available in the Elite package
- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient
Upgrade Today